

Git push command moves the changes from the local repository to a remote server. Git commit -a Pushing Changes to Remote Servers
#How to add commit and push in git on mac how to#
The following example shows how to save a snapshot of changes done in the whole working directory. This Git commit example shows how you set the description with the commit function: Git commit command takes a snapshot representing the staged changes.Īfter running the Git commit command, you need to type in the description of the commit in the text editor.
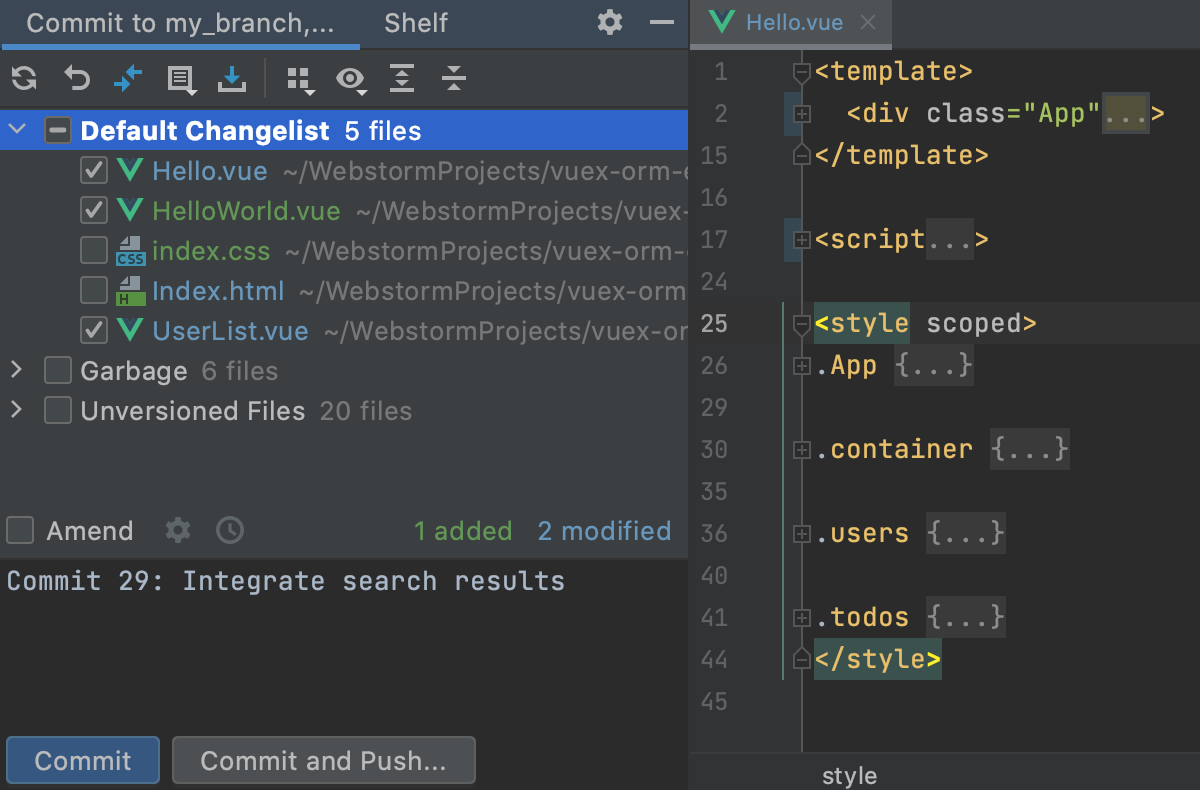
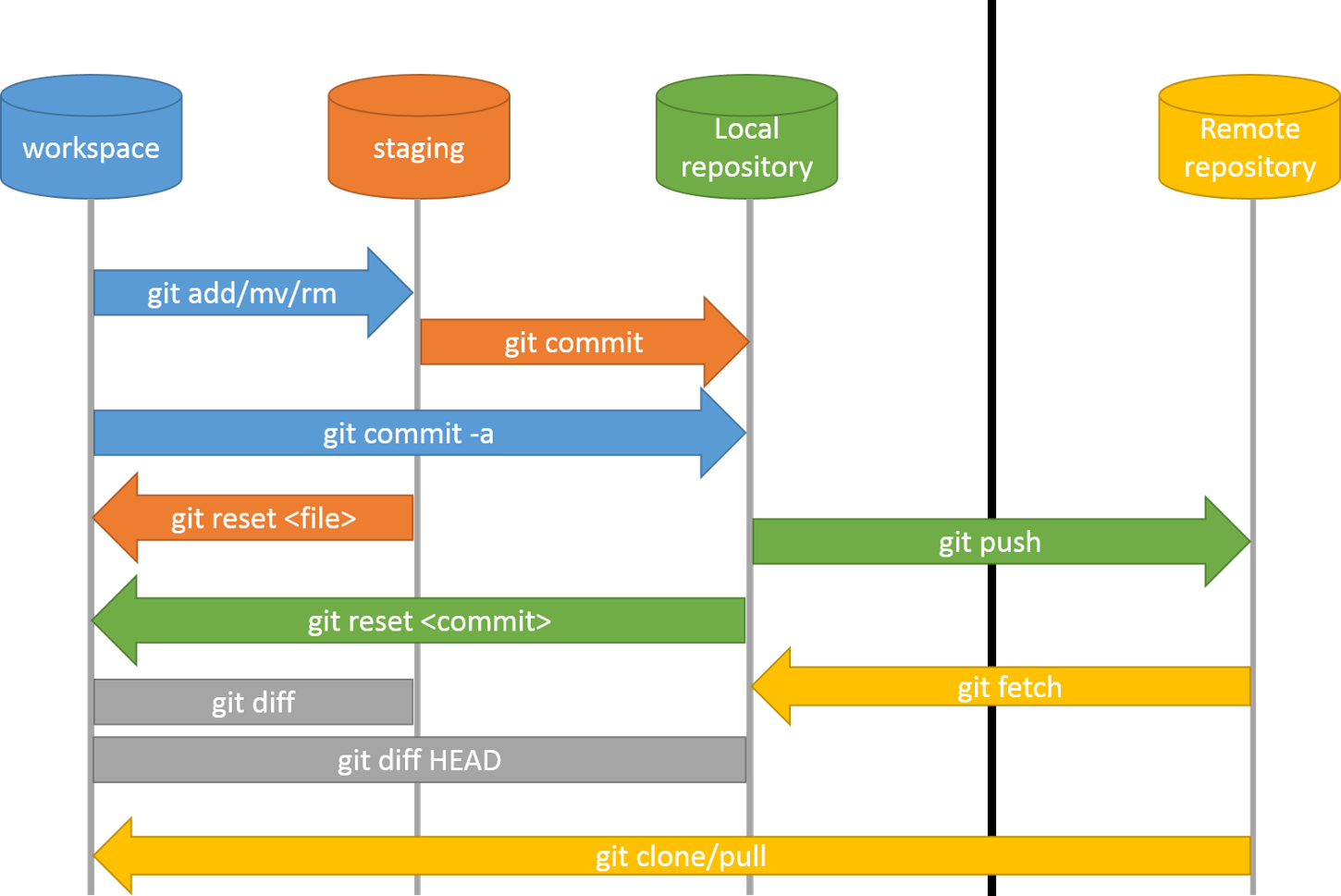
Note: do not confuse git add with svn add command. If changes are not staged for commit, they won't be saved. You need to run the Git commit command to move changes from the staging area to the local repository.Īdditionally, you may use git status command to check the status of the files and the staging area.
|- the most recent tag nameīy default, the git describe command ignores “lightweight” tags. | |- number of commits since the last tag |- the current commit is tagged with this tag name For this reason, some git commands for naming objects (like git describe) will ignore “lightweight” tags by default.Īt any time you can check if the current commit is tagged or what is the most recent tag name and how many commits ago it has been created: $ git describe “Annotated” tags are meant for releases while “lightweight” tags are meant for private or temporary object labels. Whereas a tag without tagging message is called “lightweight” tag. If you want to include a description with your tag, add -a to create an “annotated” tag: $ git tag -aĬreate an “annotated” tag with the given message (instead of prompting): $ git tag -a -m "Message"Īnnotated vs Lightweight: A Git tag created with -a option is called “annotated” tag. I will also show how to find out the most recent tag name and how many commits ago it has been created.Ĭool Tip: How to list all tags in Git! Read more → Git Create TagĬreate a “lightweight” tag on a current branch: $ git tag In this note i will show how to create a Git tag and push it remote repository using the git tag and git push commands. Tags in Git are used to label specific commits (to mark releases, for example).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
